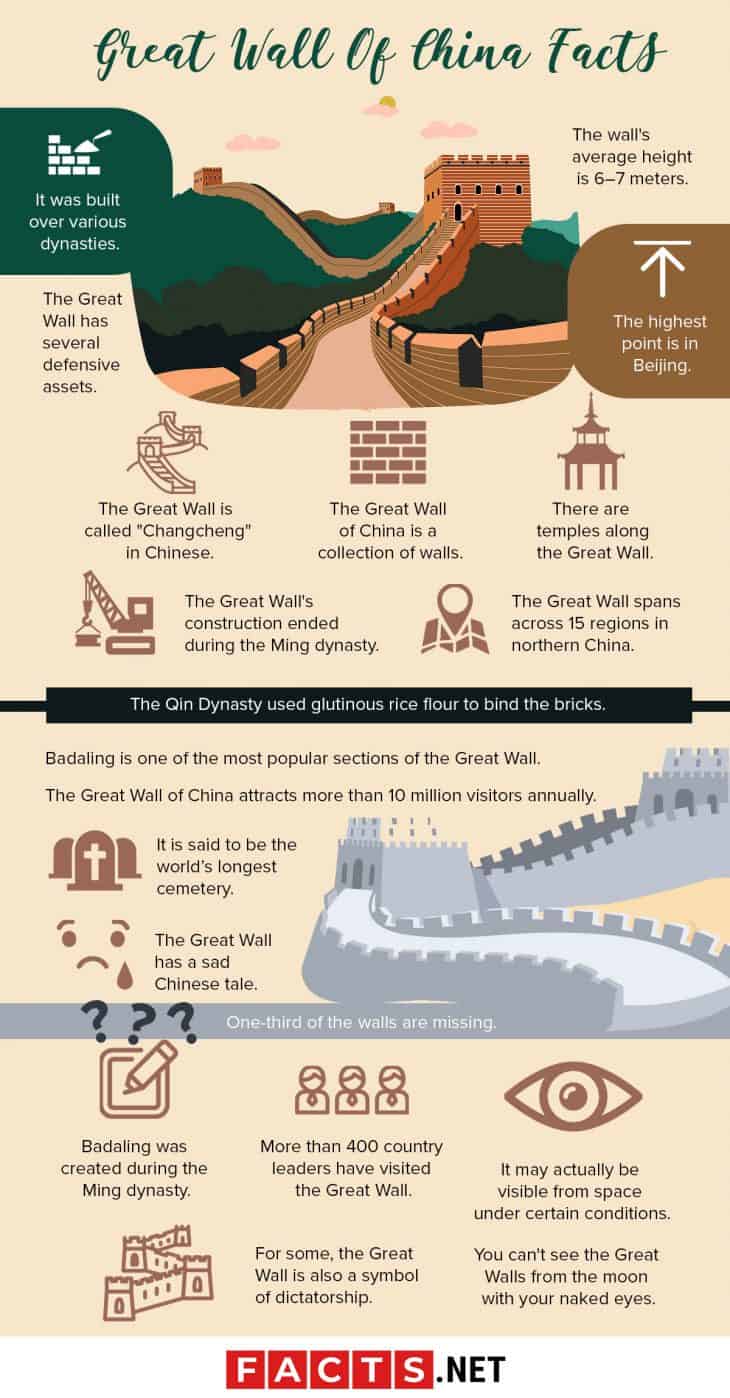
The Great Wall of China stands as one of the most impressive feats of human engineering and endurance. Commonly recognized as a symbol of Chinese culture and history, this ancient structure is surrounded by a myriad of fascinating facts. Each of these factoids not only informs but provides insight into the deeper significance and the myriad of layers that contribute to the allure of the Great Wall.
1. **An Expansive Structure**
The Great Wall stretches over 13,000 miles across northern China, making it one of the longest walls in the world. This astonishing length is not comprised of a single wall but a series of walls, trenches, and natural barriers, constructed over multiple dynasties. This complexity invites intrigue and raises questions about the historical and strategic purposes these segments were designed to serve.
2. **Construction Materials Reflecting Diversity**
A fascinating aspect of the Great Wall is the diversity of its construction materials. Depending on the local geography, builders historically employed various resources, including earth, wood, bricks, and stone. This varied use of materials not only speaks to the adaptability of ancient builders but also the rich tapestry of local cultures involved in its construction.
3. **Labor of Love**
The labor force that built the Great Wall was immense, reportedly involving millions of workers. These included soldiers, peasants, and prisoners. The sheer scale of human effort dedicated to its construction has resulted in a structure that carries the stories, hardships, and sacrifices of those who laid its foundational stones. This aspect of collective human endeavor should prompt a deeper reflection on the societal costs of monumental projects throughout history.
4. **Visibility from Space: Myth or Reality?**
A popular myth suggests that the Great Wall is visible from space with the naked eye; however, this is an exaggeration. While it is an immense structure, its colors and materials blend with the natural environment, making it difficult to discern from orbit. Yet, this misconception underscores the Wall’s iconic status and highlights our fascination with grand constructions, as they spark imaginations about human achievements against the backdrop of the universe.
5. **Defensive Architecture with Perceptive Design**
The Great Wall was designed not merely to keep enemies out but also to facilitate communication and military logistics. Watchtowers and beacon towers were strategically built at intervals along the wall to send signals regarding threats. This aspect of the Wall illustrates a layered defense strategy that was sophisticated, showcasing ingenuity in military architecture that remains worthy of study.
6. **Cultural Symbolism Beyond Military Use**
While often viewed through the lens of military defense, the Great Wall has also served as an enduring cultural symbol. It represents unity and the consolidation of various Chinese states into a singular entity. The Wall embodies national pride and identity, reflecting broader themes in Chinese history regarding resilience in the face of adversity.
7. **UNESCO World Heritage Status**
In 1987, the Great Wall was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. This recognition preserves not only the physical structure but also promotes research and education surrounding its significance. The designation is a testament to the Wall’s cultural and historical importance, encouraging global awareness and appreciation for this architectural marvel.
8. **Ongoing Preservation Challenges**
Despite its grandeur, the Great Wall faces significant preservation challenges. Erosion, climate change, and human activity threaten its structural integrity. Some sections have deteriorated to the point of being unrecognizable, prompting various conservation efforts. The ongoing dialogue about the preservation of such a historical monument invites discourse on how society prioritizes heritage in the context of modern development.
9. **A Laboratory of Architectural Styles**
The Great Wall serves as a veritable laboratory of architectural styles. Over the centuries, various dynasties contributed their unique designs and techniques, resulting in a rich amalgamation of styles ranging from simple earth mounds to majestic stone fortifications. This architectural variety not only showcases the adaption of different cultures but also reflects shifting technological advancements.
10. **Economic Impact Through Tourism**
As one of the most visited attractions in the world, the Great Wall has a formidable economic impact through tourism. Millions of visitors flock to its iconic sections like Badaling, providing revenue and creating employment opportunities for local communities. This economic activity extends beyond mere transactional exchanges, as it fosters cultural communication and global understanding.
11. **Surprising Myths and Legends**
The Great Wall is steeped in a rich tapestry of myths and legends. Stories of ghosts of those who died during its construction or tales of heroic events around its history perpetuate its mystique. These narratives hint at the Wall’s position as a cultural touchstone in Chinese folklore and highlight the intertwining of history with mythology—a commonplace phenomenon in many cultures.
12. **Environmental Integration**
Lastly, it’s essential to note how the Great Wall is not merely a man-made structure but a testament to humanity’s interaction with nature. Its construction often follows the natural contours of the land, demonstrating a respect for the environment that is critical to its enduring presence. This relationship between architecture and the natural world prompts meaningful discussions about sustainable practices in contemporary construction.
In conclusion, the Great Wall of China is much more than a physical barrier; it is an emblem of human endeavor, creativity, and resilience. Each fact contributes to a multifaceted understanding of its significance, echoing a timeless relationship between cultural heritage and the lessons of the past. These aspects make the Great Wall a source of fascination, prompting many to ponder not just its history, but its continuing legacy in the modern world.